Again a post about POJO based table , previously i have posted about-
1.Populating and adding records in POJO based table
Populate af:table programmatically from managead bean using POJO
2. Gettting selected rows from POJO based table
Get selected row (single/multiple) from POJO based table in ADF
This post is about applying sorting to POJO based table , when we drop a viewObject as af:table on page then framework provides sorting and filtering features declaratively, but when populating table from managed bean using List(POJO) then it is not there so we have to do it manually
To understand this post completely , go through previous posts and check attached application there
I have used a
PersonBean java bean class to contain columns of table or you can say there is a List of
PersonBean type that populates data in af:table. (This is the basic information about application)
Now what to do , see step by step implementation-
- Select table on page editor and create a sortListener in managed bean to handle sortEvent
- Now what we have do in sort listener ?
1.Get active sort criteria using sortEvent
2.Remove that sort criteria
3.Sort List Data Structure that is used to populate af:table
4.Apply sort criteria again on af:table
See code written in managed bean-
//List to store sort criteria
private List<SortCriterion> sortedTableList = new ArrayList<SortCriterion>();
public void setSortedTableList(List<SortCriterion> sortedTableList) {
this.sortedTableList = sortedTableList;
}
public List<SortCriterion> getSortedTableList() {
return sortedTableList;
}
/**Custom Sort Listener for POJO based af:table
* @param sortEvent
*/
public void tableSortListener(SortEvent sortEvent) {
//Get active sortCriteria on table
List<SortCriterion> activeSortCriteria = sortEvent.getSortCriteria();
SortCriterion sc = activeSortCriteria.get(0);
// Remove active criteria from table
this.removeSortCriteria(sc);
//Sort List that populates table using Comparator interface
applySortAsPerColumn(sc.getProperty());
// Add the current criteria to the list
this.sortedTableList.add(0, sc);
// Apply sort criteria to table
RichTable richTable = (RichTable) sortEvent.getComponent();
richTable.setSortCriteria(sortedTableList);
}
/**Removes sort criteria*/
private boolean removeSortCriteria(SortCriterion sortCriterion) {
//Checks that if any sortCirteria is present in list , if yes then remove it
if (sortedTableList != null && sortedTableList.size() > 0) {
for (SortCriterion sc : sortedTableList) {
if (sc.getProperty().equals(sc.getProperty())) {
sortedTableList.remove(sc);
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
Now logic to apply programmatic sort starts from here , we have to sort List using Java Comparator interface
To Read more -
How to sort ArrayList using Comparator? Comparator interface
private void applySortAsPerColumn(String criteria) {
//Get List that populates table
List<PersonBean> list = getPersonList();
//Check which column's sorting is triggered from UI
//and then sort list on basis of that attribute
//Sorting of collection makes use of Comparator interface, Read about it
if ("name".equalsIgnoreCase(criteria)) {
Collections.sort(list, new ProgTableBean.PersName());
} else if ("mobNo".equalsIgnoreCase(criteria)) {
Collections.sort(list, new ProgTableBean.MobNo());
} else if ("salary".equalsIgnoreCase(criteria)) {
Collections.sort(list, new ProgTableBean.Salary());
}
}
// Comparator for all attributes to sort List according to different attributes
public static class PersName implements Comparator<PersonBean> {
private int flag = 1;
@Override
public int compare(PersonBean o1, PersonBean o2) {
return flag * o1.getName().compareTo(o2.getName());
}
}
public static class MobNo implements Comparator<PersonBean> {
private int flag = 1;
@Override
public int compare(PersonBean o1, PersonBean o2) {
System.out.println("In 2**");
return flag * o1.getMobNo().compareTo(o2.getMobNo());
}
}
public static class Salary implements Comparator<PersonBean> {
private int flag = 1;
@Override
public int compare(PersonBean o1, PersonBean o2) {
return flag * o1.getSalary().compareTo(o2.getSalary());
}
}
- Now on page ,select table and set sortable true for each column and set sortProperty same as column name
Check af:table source after setting all properties
<af:table var="row" rowBandingInterval="1" id="t1" value="#{viewScope.ProgTableBean.personList}"
partialTriggers="::b1" rowSelection="multiple" binding="#{viewScope.ProgTableBean.tableBind}"
selectionListener="#{viewScope.ProgTableBean.tableSelection}"
sortListener="#{viewScope.ProgTableBean.tableSortListener}">
<af:column sortable="true" headerText="Name" id="c1" width="150" sortProperty="name">
<af:outputText value="#{row.name}" id="ot1"/>
</af:column>
<af:column sortable="true" headerText="Mobile Number" id="c2" sortProperty="mobNo">
<af:outputText value="#{row.mobNo}" id="ot2"/>
</af:column>
<af:column sortable="true" headerText="Salary" id="c3" align="right" sortProperty="salary">
<af:outputText value="#{row.salary}" id="ot3"/>
</af:column>
</af:table>
- All done :) , Run and check application
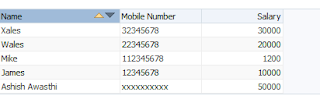
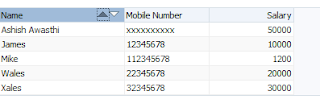
Sample ADF Application -Download
Cheers :) Happy Learning





